In the vast canvas of the night sky, certain celestial entities captivate our gaze with their brilliance and intrigue. Among these luminous wonders stands Aldebaran, a beacon of celestial grandeur nestled within the constellation of Taurus. Join me as we embark on a journey to unravel the mystique surrounding this remarkable star.
The Bright Jewel of Taurus
Aldebaran, also known as Alpha Tauri, emerges as the brightest star in the Taurus constellation, captivating stargazers with its radiant glow. Its name, derived from Arabic roots, translates to "the follower," as it appears to follow the Pleiades star cluster across the night sky. With an apparent magnitude of approximately 0.85, Aldebaran proudly earns its place among the twenty brightest stars visible from Earth.
Characteristics
Aldebaran, the luminous heart of the Taurus constellation, captivates with its distinctive traits as an orange giant star. With a mass of approximately 1.16 times that of our Sun and a radius extending to about 45.1 times that of our solar system's central star, Aldebaran commands a formidable presence in the celestial expanse. Radiating with a luminosity approximately 500 times greater than the Sun, its majestic glow illuminates the night sky with a reddish-orange hue, a testament to its cooler temperature of 3900 Kelvin. Aldebaran's cosmic dance unfolds over a leisurely rotational period of approximately 520 days, adding a rhythmic cadence to its celestial journey. Hosting a variable star companion known as Alpha Tauri B, Aldebaran reveals itself as a celestial luminary of unparalleled beauty and intrigue, inviting stargazers to ponder the mysteries of the cosmos.
A Spectrum of Splendor
One cannot help but marvel at Aldebaran's captivating hue, reminiscent of a fiery ember ablaze in the heavens. This distinctive reddish-orange tint stems from the star's classification as a K-type giant, signifying its advanced evolutionary stage. As a result of its expanded outer layers, Aldebaran radiates warmth and brilliance, inviting contemplation of the cosmic forces at play within its luminous embrace.
Proximity and Parallax
Despite its celestial grandeur, Aldebaran resides a mere 65 light-years from Earth, making it a relatively close neighbor in astronomical terms. This proximity allows astronomers to study Aldebaran's properties with exceptional detail, shedding light on its composition, temperature, and evolutionary trajectory. Through precise measurements of parallax, scientists have gleaned invaluable insights into the stellar dynamics that govern our universe.
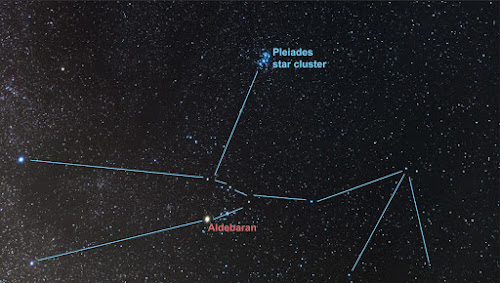
If you want to find Aldebaran, then you can take the help of Orion Belt stars, on the left of which Aldebaran is the brightest star in the Taurus constellation. You can also blur it with the help of Hyades and Pleiades clusters, although it is not in the Hyades cluster, still you will feel that it is in the Hyades cluster, you can blur it with the help of V shape, you can see it in the photo below.
Aldebaran B
Aldabaran B, also known as Alpha Tauri B, is a gas-living planet of the Aldabaran system which is slightly larger than Jupiter. It orbits the Aldabaran star so closely that no remains of water have been found in it. If you want to see it, you will need a very powerful telescope because it is not visible at all in the light of Aldabaran. One year here is equal to 1.7 years on Earth.
Mythology and Cultural Significance
Throughout the annals of human history, Aldebaran has held a place of reverence in myriad cultures and civilizations. In ancient Mesopotamian mythology, it featured prominently as the "Eye of Taurus," symbolizing the watchful gaze of divine beings. Similarly, in Greek mythology, Aldebaran represented the fiery eye of the bull slain by the hero Perseus, immortalizing its celestial prominence in the tapestry of legends.
Stellar Evolution and Future Prospects
As a K-type giant star, Aldebaran finds itself in the twilight of its stellar evolution. Having exhausted its reserves of hydrogen fuel, it now embarks on a transformative journey towards its ultimate fate. In the eons to come, Aldebaran will shed its outer layers in a spectacular display of cosmic rejuvenation, casting off its mortal shell to reveal the radiant core that lies beneath.
Conclusion: A Celestial Symphony
In the vast expanse of the cosmos, Aldebaran stands as a testament to the enduring beauty and complexity of the universe. Its radiant splendor illuminates the heavens, inviting us to ponder the mysteries of creation and the interconnectedness of all things. As we gaze upon this celestial jewel, may we find inspiration in its timeless allure and forge a deeper connection with the cosmic symphony that surrounds us.
In the grand tapestry of the cosmos, Aldebaran shines as a radiant testament to the beauty and complexity of the universe, inviting us to contemplate the mysteries of creation and our place within the celestial dance of the cosmos.



%20-%201.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment