Betelgeuse: One of the brightest star will going to disappear
In the vast expanse of the night sky, amidst the twinkling stars, Betelgeuse shines bright as one of the nearest and most captivating celestial bodies in the Orion constellation. Its reddish hue and immense size make it a standout feature, known for its variability and potential for a spectacular supernova explosion. Let's delve deeper into the fascinating world of Betelgeuse and explore its significance in the cosmos.
Betelgeuse: A Star of Distinction
Named after the Arabic phrase meaning "the armpit of the central one," Betelgeuse holds a special place in the lore and science of astronomy. As a red supergiant star, it boasts a diameter over a thousand times that of our Sun, making it one of the largest stars known to humanity. Its luminosity and proximity have made it a prominent feature in the night sky, captivating astronomers and stargazers for centuries.
Diving into Betelgeuse's Dynamics
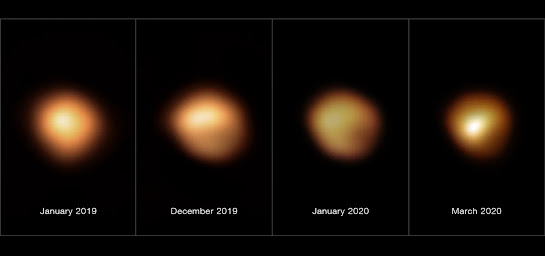
What sets Betelgeuse apart is its dynamic nature. Unlike stable stars, Betelgeuse experiences fluctuations in its brightness over various timescales, ranging from weeks to years. These changes, attributed to its pulsations and surface activity, add to its mystique and provide valuable insights into the life cycle of massive stars. Studying these fluctuations has become a focal point for astronomers seeking to unravel the mysteries of stellar evolution.
The Specter of Supernova: Betelgeuse's Impending Explosion
As Betelgeuse nears the end of its stellar journey, astronomers eagerly anticipate its inevitable fate: a supernova explosion. Given its massive size and advanced stage of evolution, Betelgeuse is primed to undergo this cataclysmic event in the cosmic timeline. When it occurs, Betelgeuse's supernova will shine with an intensity surpassing that of the entire Milky Way galaxy, offering a rare opportunity for scientists to witness and study such an event in real-time.
Unlocking Cosmic Mysteries: The Scientific Impact of Betelgeuse's Supernova
The impending supernova of Betelgeuse holds immense scientific significance. By observing and analyzing the aftermath of this explosive event, astronomers hope to gain valuable insights into various astrophysical phenomena. From the formation of heavy elements to the dynamics of stellar explosions, Betelgeuse's supernova promises to enrich our understanding of the universe's fundamental processes and cosmic evolution.
Beyond the Supernova: Betelgeuse's Legacy in the Cosmos
Even after its inevitable explosion, Betelgeuse will continue to leave a lasting legacy in the annals of astronomy. Its supernova remnants will serve as cosmic laboratories for studying the aftermath of stellar explosions, contributing to our knowledge of galactic dynamics and the synthesis of elements crucial for life. Moreover, Betelgeuse's demise will inspire future generations of astronomers to explore the mysteries of the universe and unravel the secrets hidden within the stars.
In conclusion, Betelgeuse stands as a beacon of cosmic wonder, illuminating the night sky and igniting our curiosity about the universe's vast mysteries. As we await its spectacular supernova, let us marvel at the beauty and complexity of this stellar giant and reflect on the profound insights it offers into the nature of the cosmos.
Compare the brightness of the star year by year
These images, taken with the SPHERE instrument on ESO's Very Large Telescope
Image of betelgeuse
(Image credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/E. O’Gorman/P. Kervella)


Comments
Post a Comment